Can EECP Therapy Remove Blockages ?
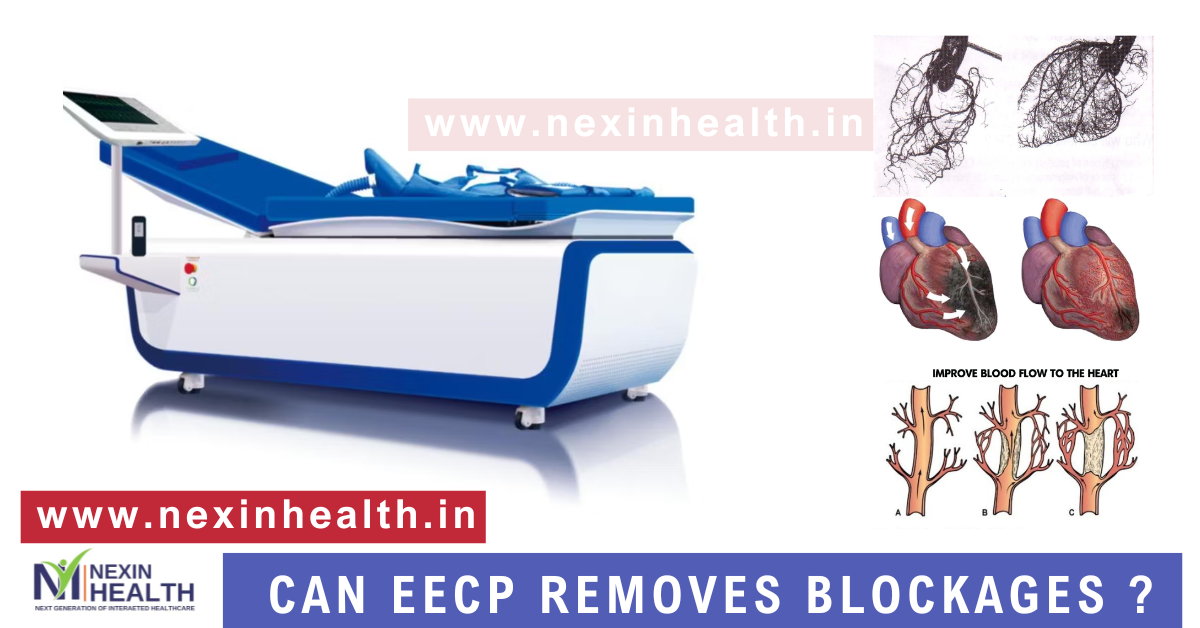

Can EECP Therapy Remove Blockages: Arterial plaque buildup is a leading cause of heart disease, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular issues. As more people search for non-invasive alternatives to surgery for managing arterial blockages, Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) therapy has gained attention. While EECP therapy doesn’t directly “remove” arterial plaque, it offers a unique approach to managing coronary artery disease by improving blood flow, creating new collateral vessels, and enhancing the function of existing arteries.
In this blog, we’ll explore what arterial plaque is, how it forms, and how EECP therapy can help manage its effects without the need for invasive surgery. We will also delve into what patients often misunderstand about EECP treatment and plaque removal, and why this therapy is a safer and more natural option for treating coronary blockages.
Watch Video:
Arterial plaque is a combination of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances that accumulate in the walls of the arteries. Over time, this buildup causes the arteries to narrow and harden, reducing blood flow to vital organs, including the heart. This condition is commonly known as atherosclerosis, and when it affects the arteries supplying the heart, it’s referred to as coronary artery disease (CAD).
Plaque begins to form when cholesterol and other substances in the blood adhere to the artery walls. Over time, these deposits grow, creating blockages that impede blood flow. The body’s immune response to this buildup can cause inflammation, which makes the plaque even more unstable and prone to rupture. When plaque ruptures, it can lead to the formation of a blood clot that completely blocks the artery, causing a heart attack or stroke.
Arterial plaque consists of several components:
Plaque is categorized into several types:
EECP therapy is a non-invasive treatment designed to improve blood circulation in patients with heart disease. During EECP therapy, inflatable cuffs are placed around the legs and thighs. These cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the heartbeat, enhancing blood flow back to the heart and encouraging the formation of new blood vessels, called collateral circulation. This process improves the heart’s oxygen supply, reduces chest pain (angina), and enhances overall cardiovascular function.
Although EECP therapy does not directly remove plaque, it helps manage coronary blockages in several ways:
By enhancing collateral vessel formation and improving blood flow, EECP therapy alleviates the symptoms caused by coronary blockages, such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath. While it doesn’t physically remove plaque, the improved circulation allows oxygen-rich blood to reach areas that were previously deprived due to blockages. This reduces the workload on the heart and can prevent further deterioration of heart function.
One common misconception among patients is that EECP therapy can remove arterial plaque. However, EECP therapy doesn’t directly clear plaque from the arteries. Instead, it works by improving blood flow around blocked arteries and encouraging the formation of new blood vessels. It is a natural bypass process rather than a plaque-removal procedure like angioplasty or stenting.
During EECP treatment, cuffs wrapped around the patient’s legs inflate and deflate in sync with the heart’s rhythm. This action enhances venous return to the heart, pushing more oxygen-rich blood into coronary arteries and other parts of the body. Over time, this repeated pressure stimulates angiogenesis and improves the overall health of the blood vessels, creating new pathways for blood flow.
Patients with angina (chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart) and heart failure often experience significant relief from symptoms after completing EECP therapy. The improved blood flow decreases the frequency and severity of chest pain, while enhanced circulation reduces the heart’s workload, improving overall heart function in heart failure patients.
EECP therapy offers several advantages over invasive procedures such as bypass surgery or angioplasty:
EECP therapy typically lasts for one hour per session and is performed five days a week for seven weeks. Patients lie down on a comfortable table while cuffs are wrapped around their legs. These cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the patient’s heartbeat, encouraging blood flow back to the heart.
Heart surgery—whether bypass surgery or angioplasty—involves invasive techniques to physically remove or bypass plaque. In contrast, EECP is a natural, non-invasive treatment that encourages the heart to create its own bypass through the formation of new blood vessels. While surgery addresses the immediate blockage, EECP strengthens overall circulation and improves heart health without the risks associated with surgical procedures.
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells lining the blood vessels, playing a crucial role in regulating blood flow and reducing inflammation. EECP therapy has been shown to improve endothelial function by stimulating the release of nitric oxide, which helps relax blood vessels, reduces inflammation, and prevents the formation of new plaque.
EECP therapy is widely accepted across the globe as an effective treatment for coronary artery disease, heart failure, and angina. It has received approval from medical authorities such as the FDA in the United States and is widely used in countries like India, China, Germany, and Canada.
Numerous studies and clinical trials have demonstrated the benefits of EECP therapy in improving heart function, reducing angina symptoms, and enhancing quality of life in patients with heart disease. Research continues to explore its potential in managing other conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
Read More:
Can EECP Treatment Replace Bypass Surgery:
Can EECP Treatment Prevent the Risk of Heart Attack: