EECP Therapy vs. Angioplasty: Which is Better for Your Heart Health?
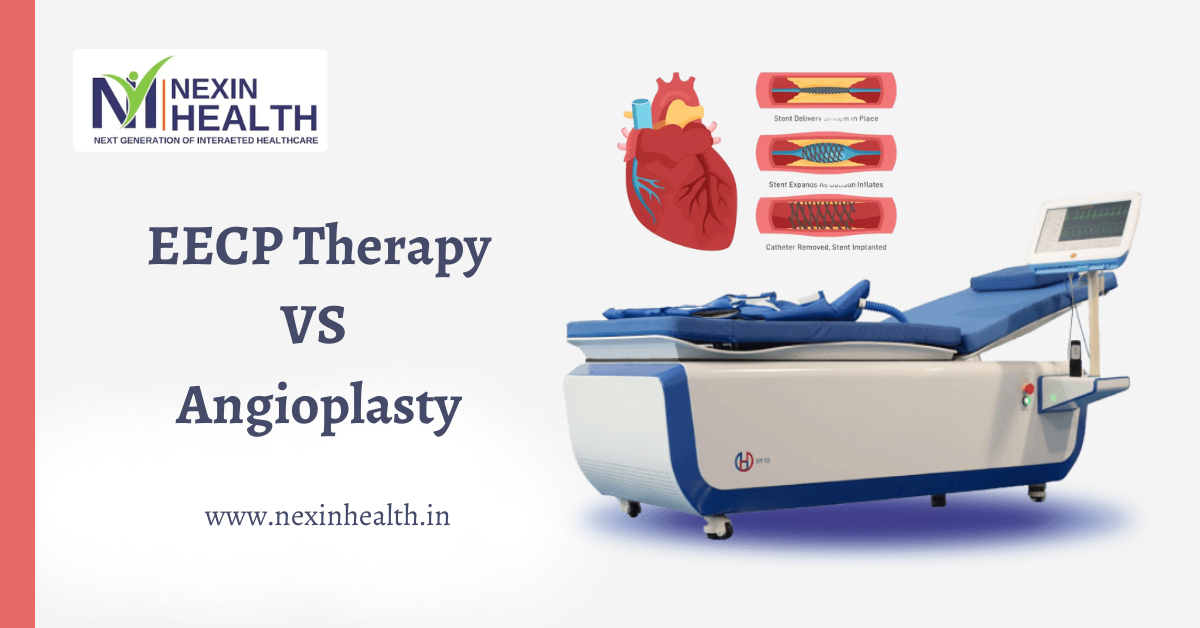

EECP Therapy vs. Angioplasty: When it comes to heart health, choosing the right treatment can be life-changing. Two popular treatments for coronary artery disease (CAD) are /EECP therapy and angioplasty. While both aim to improve blood flow to the heart, they differ significantly in approach, risks, and benefits.
In this blog, we will explore the key differences between EECP therapy and angioplasty, helping you make an informed decision about your heart health.
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) therapy is a non-invasive treatment designed to increase blood flow to the heart by improving the development of collateral circulation. This therapy involves the use of cuffs wrapped around the lower body that inflate and deflate in sync with the heartbeat. As a result, blood is pushed back to the heart, enhancing coronary perfusion.
More Read:
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a surgical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. A catheter with a small balloon at the tip is inserted into the blocked artery, and the balloon is inflated to widen the artery. Often, a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
| Factors | EECP Therapy | Angioplasty |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Non-invasive | Invasive (surgical) |
| Recovery Time | Immediate | Days to weeks |
| Effectiveness | Improves collateral circulation | Restores blood flow immediately |
| Cost | Relatively low | Higher due to hospital charges |
| Risks | Minimal | Risk of bleeding, infection, artery damage |
| Long-Term Outcome | Gradual improvement | Immediate but may require repeat procedures |
Choosing between EECP therapy and angioplasty depends on several factors such as the severity of the blockage, overall health, and patient preference. Here’s how to decide:
For more information on non-invasive EECP treatments, visit EECP Treatment in India.

1. Is EECP therapy as effective as angioplasty?
EECP therapy is effective for patients with mild to moderate CAD, while angioplasty is preferred for severe blockages. Both have their merits depending on the patient’s condition.
2. Can EECP therapy replace angioplasty?
In some cases, EECP therapy can serve as an alternative for patients who are not ideal candidates for surgery. However, it may not be suitable for life-threatening blockages.
3. What are the side effects of EECP therapy?
EECP is generally safe, but some patients may experience leg discomfort, bruising, or muscle aches during treatment.
4. How long does EECP therapy take?
A typical EECP therapy regimen consists of one-hour sessions, five days a week, for seven weeks.
5. Is angioplasty a permanent solution?
While angioplasty can restore blood flow, the effects may not be permanent, and some patients may require repeat procedures.
6. Which option is more affordable?
EECP therapy is generally more affordable compared to angioplasty, especially when considering hospital and recovery costs.
EECP therapy and angioplasty each have their own advantages and limitations. While angioplasty is suitable for severe cases requiring immediate intervention, EECP therapy offers a non-invasive and gradual approach to improving heart health. Always consult with your cardiologist to choose the best option for your specific condition.
Also Read: