The Powerful Guide to Heart Failure and Its Long Term Complications
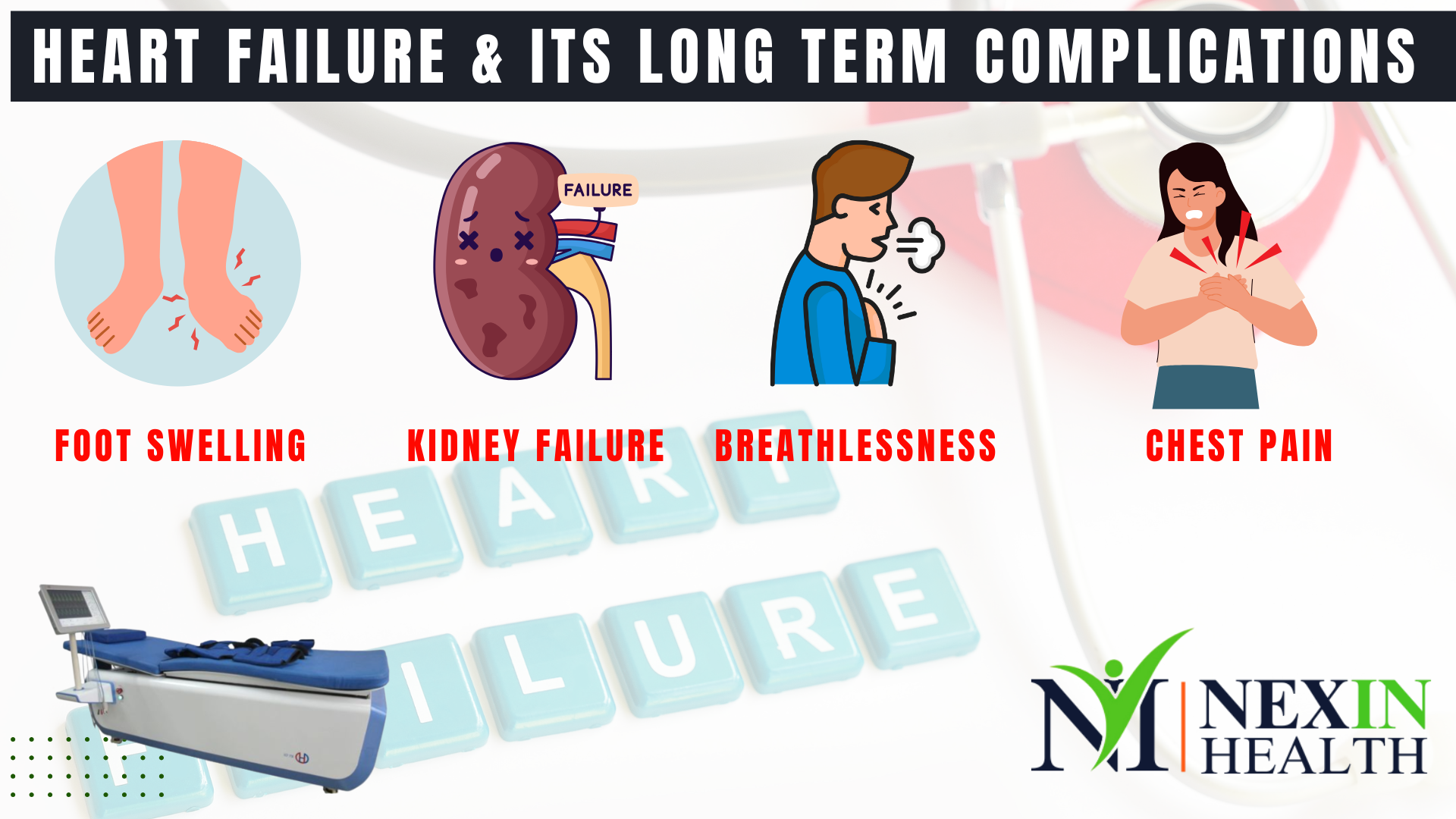

The Powerful Guide to Heart Failure and Its Long Term Complications: Have you or someone close to you in India been told about heart failure? It’s a condition that affects many, making the heart struggle to pump blood effectively. While the term itself can sound alarming, understanding heart failure – its causes, how it affects the body over time (long term complications of heart failure), and the ways to manage it – is the first powerful step towards living a better and longer life.
Think of your heart as a tireless worker, constantly supplying your body with the energy it needs. In heart failure, this worker gets weakened or stiff, making it harder to do its job. This can lead to various problems, not just with the heart itself, but also affecting other important parts of your body in the long run. Knowing about these potential long term complications of heart failure is like having a map for a challenging journey – it helps you anticipate what might come and how to navigate it.
Why is this knowledge so vital for us in India? With a growing number of people affected by heart conditions, understanding heart failure is crucial for patients, families, and caregivers. This comprehensive guide will break down heart failure and its long term complications in health in simple terms. We will explore the reasons why it happens, the different types, how it’s graded, the potential long-term risks, and most importantly, how to live a healthier and longer life with heart failure through various treatment options available in India.
In this powerful guide, we will explore:
Living with heart failure requires understanding and proactive management. This guide aims to empower you with the knowledge to live stronger and longer. Let’s begin this important journey together.
As we discussed, heart failure doesn’t mean the heart has stopped. It means the heart muscle is weakened or stiff and can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs for oxygen and nutrients. This can happen gradually over time or suddenly after a heart event. Because the heart’s job is so vital, its struggle can lead to a cascade of problems throughout the body, especially in the long term.
The heart has four main chambers: two upper chambers (atria) that receive blood and two lower chambers (ventricles) that pump blood out. Heart failure can affect either the left side (which pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body), the right side (which pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs), or both sides of the heart. Understanding which part of the heart is affected is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Your heart has four chambers: two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).

The left ventricle is the main pumping chamber, responsible for sending oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body. The strength of the left ventricle’s pumping action is measured by a value called LVEF (Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction). A normal LVEF is around 55-70%. When the LVEF decreases, it means the heart’s pumping ability is compromised.
Common Causes of Heart Failure: What Weakens the Heart?
Several conditions can damage or weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to heart failure. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective management. Some common causes of heart failure include:
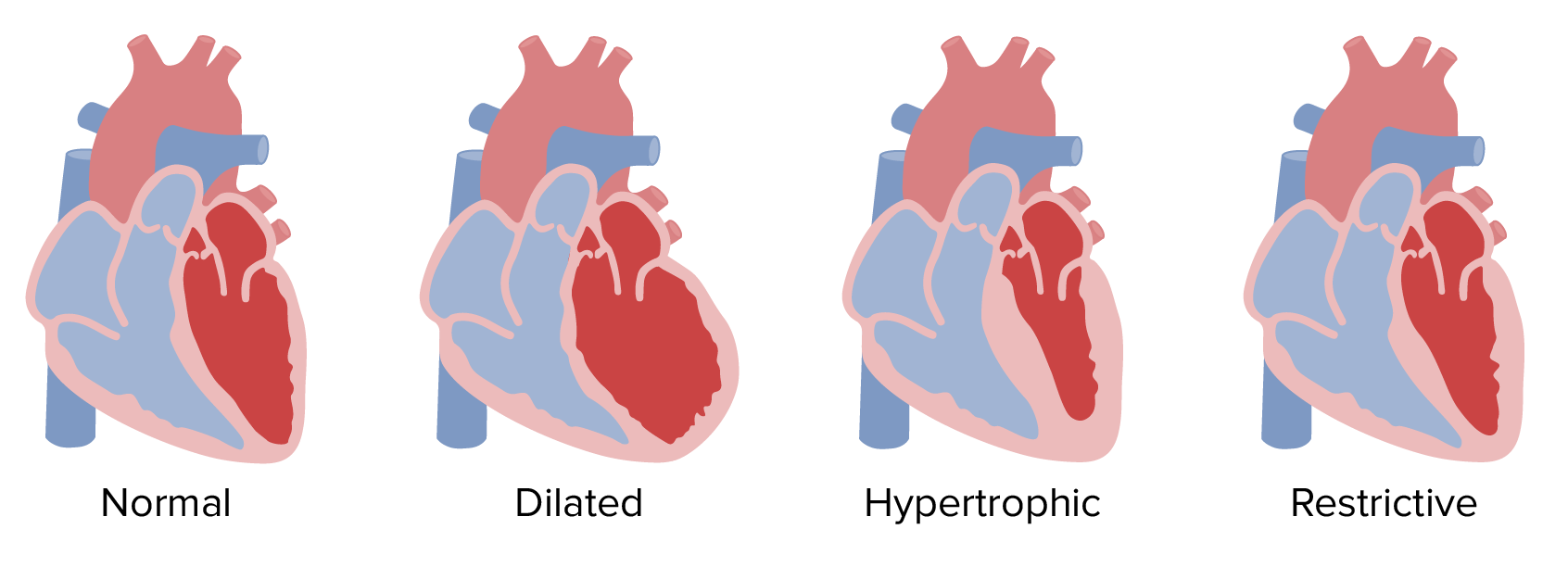
Cardiomyopathy is a general term for diseases of the heart muscle. These conditions can change the size, shape, or thickness of the heart muscle, making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively and leading to heart failure. There are several types of cardiomyopathy:
Understanding the specific type of cardiomyopathy is important for guiding treatment and managing the risk of long term complications of heart failure.
Heart failure can also be classified based on which side of the heart is primarily affected and how the heart muscle is functioning:
Understanding the type of heart failure helps doctors tailor the treatment approach and anticipate potential long term complications of heart failure.
The ejection fraction (EF) is a key measurement used to assess the severity of systolic heart failure. It represents the percentage of blood that the left ventricle pumps out with each beat. Here’s a simplified table showing the grades of heart failure based on ejection fraction:
| Grade | Ejection Fraction (EF) | What it Means |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 50% – 70% | The heart is pumping a healthy amount of blood. |
| Mildly Reduced (Borderline) | 41% – 49% | The heart is pumping slightly less blood than normal. |
| Moderately Reduced | 30% – 40% | The heart is pumping a reduced amount of blood. |
| Severely Reduced | Less than 30% | The heart is pumping a significantly reduced amount of blood. |
It’s important to note that even with a “normal” ejection fraction (in diastolic heart failure), the heart isn’t functioning optimally. The EF is primarily used to classify systolic heart failure. The grade of heart failure based on ejection fraction helps doctors understand the severity of the condition and the potential risk of increased mortality rate risk and long term complications of heart failure.
Read Also: EECP Therapy for Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious condition associated with a significant increased mortality rate risk. The prognosis for individuals with heart failure can vary depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition (as indicated by the NYHA functional classification, which we will discuss later if space permits, and ejection fraction), the presence of other health problems, and how well the condition is managed.
Studies worldwide have consistently shown that the mortality rate for heart failure patients is higher compared to the general population. The risk of death increases with the severity of heart failure and the presence of long term complications of heart failure like kidney disease, arrhythmias, and cardiac cachexia.
For example, research has shown that the 5-year survival rate after a diagnosis of heart failure is around 50%, meaning that about half of the people diagnosed with heart failure will still be alive after five years. This highlights the seriousness of the condition and the importance of early diagnosis, effective management, and prevention of long term complications of heart failure to improve survival rates.
Understanding the increased mortality rate risk associated with heart failure underscores the urgency of taking proactive steps to manage the condition and adopt a lifestyle that supports heart health.
While heart failure is a serious condition, it doesn’t mean you can’t live a fulfilling and longer life. By actively participating in your care and making positive lifestyle changes, you can significantly improve your quality of life and potentially increase your lifespan. Here’s how to live healthy and longer with heart failure:
By actively embracing these strategies, individuals with heart failure in India can take control of their health, manage their symptoms effectively, reduce the risk of long term complications of heart failure, and strive for a healthier and longer life.
Managing heart failure involves a multi-faceted approach that includes medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes medical devices or procedures. The specific treatment options for heart failure will depend on the cause, type, and severity of your condition. Here’s an overview of the common treatment options:
The choice of treatment options for heart failure will be made by your cardiologist based on a thorough evaluation of your individual condition. It’s important to discuss all available options and their potential benefits and risks with your doctor.
When dealing with a weakened heart, different approaches focus on various aspects of care. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Feature | Heart Failure Management (Comprehensive) | Treating Underlying Cause (e.g., CAD Treatment) | Symptom Management (e.g., Angina Relief) | End-Stage Care (e.g., Palliative Care) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Improve heart function, manage symptoms, prevent complications | Address the root cause of heart weakening | Relieve immediate symptoms like pain or breathlessness | Improve comfort and quality of life in advanced stages |
| Focus | Holistic (meds, lifestyle, devices) | Specific condition causing heart failure | Immediate relief of discomfort | Comfort, emotional support |
| Examples | ACE inhibitors, diet changes, ICD | Angioplasty for CAD, blood pressure control | Nitrates for angina, diuretics for fluid | Pain management, emotional counseling |
| Long-Term Impact | Aims to improve survival and quality of life | Can prevent further heart damage and progression to heart failure | Improves immediate well-being | Provides support and dignity in final stages |
.
The choice of treatment options for heart failure will be made by your cardiologist based on a thorough evaluation of your individual condition. It’s important to discuss all available options and their potential benefits and risks with your doctor.
When dealing with a weakened heart, different approaches focus on various aspects of care. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Feature | Heart Failure Management (Comprehensive) | Treating Underlying Cause (e.g., CAD Treatment) | Symptom Management (e.g., Angina Relief) | End-Stage Care (e.g., Palliative Care) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Improve heart function, manage symptoms, prevent complications | Address the root cause of heart weakening | Relieve immediate symptoms like pain or breathlessness | Improve comfort and quality of life in advanced stages |
| Focus | Holistic (meds, lifestyle, devices) | Specific condition causing heart failure | Immediate relief of discomfort | Comfort, emotional support |
| Examples | ACE inhibitors, diet changes, ICD | Angioplasty for CAD, blood pressure control | Nitrates for angina, diuretics for fluid | Pain management, emotional counseling |
| Long-Term Impact | Aims to improve survival and quality of life | Can prevent further heart damage and progression to heart failure | Improves immediate well-being | Provides support and dignity in final stages |
It’s crucial to understand that these approaches often overlap. Managing heart failure involves treating the underlying cause if possible, alleviating symptoms, and providing comprehensive care to improve the patient’s long-term well-being.
Understanding heart failure and its long term complications is crucial for a wide range of individuals:
In essence, anyone whose life is touched by heart failure, directly or indirectly, can benefit from understanding this complex condition and its potential long-term impact.
Living well with heart failure is an ongoing process that requires a proactive and informed approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help navigate this journey:
By following these steps, individuals with heart failure in India can navigate their condition more effectively, manage potential long term complications of heart failure, and strive for a better quality of life.
Numerous studies and real-world examples underscore the importance of proactive management in improving outcomes for heart failure patients:
These studies highlight the significant impact of evidence-based treatments and proactive lifestyle management in helping individuals with heart failure live longer and better lives. Real-world case studies of individuals who diligently follow their treatment plans and adopt healthy lifestyles often demonstrate remarkable improvements in their symptoms, functional capacity, and overall well-being.
Que: Is heart failure a death sentence? Ans: No, while heart failure is a serious condition, it is often a chronic illness that can be managed effectively for many years with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. Many people with heart failure live active and fulfilling lives.
Que: What are the early warning signs of worsening heart failure? Ans: Early signs can include increased shortness of breath, new or worsening swelling in the legs or ankles, unexplained weight gain, increased fatigue, and persistent cough or wheezing. It’s important to report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor promptly.
Que: Can lifestyle changes alone cure heart failure? Ans: No, while lifestyle changes are crucial for managing heart failure and preventing long term complications of heart failure, they cannot cure the condition. Medications and sometimes devices or procedures are also necessary.
Que: What is the role of diet in managing heart failure? Ans: A heart-healthy, low-sodium diet is essential for managing heart failure. Limiting sodium helps prevent fluid retention, which can worsen symptoms. Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall heart health.
Que: How much exercise is safe for someone with heart failure? Ans: The amount and intensity of exercise should be determined in consultation with your doctor or a cardiac rehabilitation specialist. Gentle, regular exercise like walking is usually encouraged, but it’s important to avoid overexertion.
Que: Are there any alternative therapies that can help with heart failure? Ans: While some alternative therapies like yoga and meditation can help manage stress, which is beneficial for heart failure, they should not replace conventional medical treatments. Always discuss any alternative therapies with your doctor. EECP is a non-invasive therapy with some evidence of benefit for heart failure symptoms.
Que: What should I do if I miss a dose of my heart failure medication? Ans: Do not double the next dose. Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next scheduled dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular 1 schedule. Always clarify specific instructions with your doctor or pharmacist.
Living with heart failure presents challenges, but with knowledge, proactive management, and a strong partnership with your healthcare team, you can live a more fulfilling and potentially longer life. Understanding the causes of heart failure, the different types and grades, the potential for long term complications of heart failure, and the various treatment options available empowers you to take control of your health journey.
Remember that you are not alone. Millions of people around the world, including in India, are living with heart failure. By embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, adhering to your medical treatment plan, and staying informed, you can navigate this condition effectively and strive for a better quality of life. Take heart, be proactive, and live stronger, longer.
Ready to take powerful control of your heart health and live stronger with heart failure?
Ready to take powerful control of your heart health and live stronger with heart failure?
Contact us today for personalized guidance and support at
NEXIN HEALTH!
Call or WhatsApp: +91 9310145010