Can High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack? Risks, Symptoms & Natural Treatments
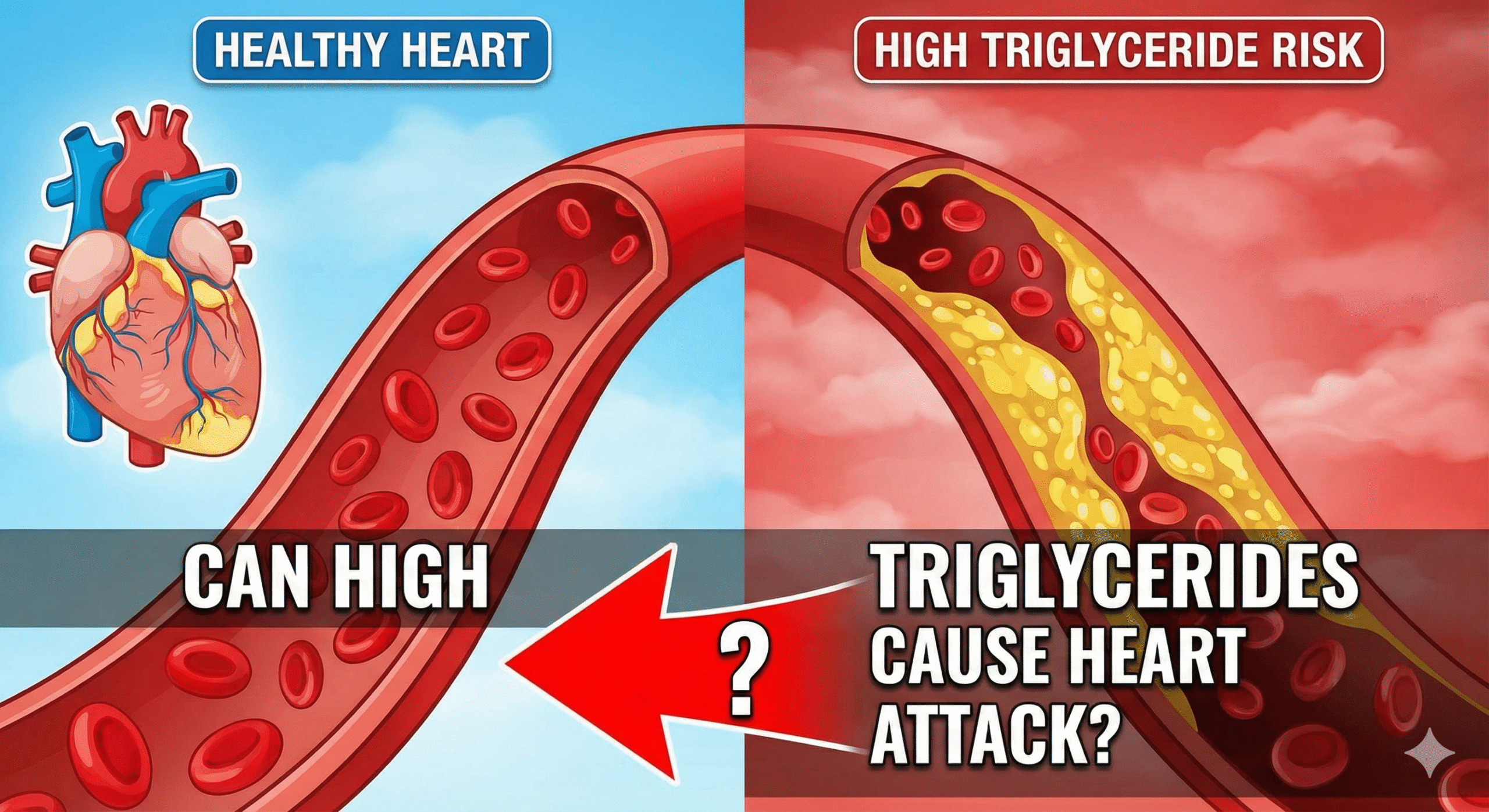

Can High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack?
In the world of heart health, we often hear about the dangers of cholesterol. It is the villain in almost every story about heart disease. However, there is another silent threat floating in your blood, often ignored or misunderstood, that is just as dangerous. This threat is triglycerides. Many patients come to us with “normal” cholesterol levels but still suffer from angina, blocked arteries, or even heart attacks. The missing piece of the puzzle is often this specific type of fat.
You are likely here because you have seen a high number on your lab report, or perhaps a doctor has warned you about your lipid profile. You have a burning question: Can High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack? The answer, supported by decades of research and the latest clinical findings in 2024 and 2025, is a definitive yes.
High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack not by magic, but by a specific biological process that thickens your blood, inflames your artery walls, and builds stubborn plaque that restricts blood flow to your heart. For patients managing diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or existing heart disease, understanding this connection is not just optional—it is a matter of survival.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your encyclopedia. We will break down exactly how High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack, exploring the science in simple language. We will look at why winter mornings are particularly dangerous for people with high levels, how natural remedies like Arjuna and Garlic can help, and how advanced non-invasive therapies like EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) offer a “natural bypass” for those seeking to avoid surgery.
Before we dive deep into the science and solutions, let’s look at some eye-opening facts. These are critical pieces of information that explain why High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack and why you must take action today.
DID YOU KNOW?
The “Residual Risk” Reality: Even if you take statins to lower your bad cholesterol (LDL) to perfect levels, you still have a high risk of a heart event if your triglycerides remain high. This is called “residual risk.” Recent studies confirm that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack even in people with low cholesterol.
Sugar, Not Fat, is the Culprit: Contrary to popular belief, eating fat isn’t the main reason for high triglycerides. The liver converts excess sugar and refined carbohydrates (like bread, rice, and biscuits) directly into triglycerides. If you are a diabetic, your high blood sugar is essentially turning into blood fat.
The “Morning Heart Attack” Danger: High triglycerides make your blood more viscous (thicker). Research from 2025 highlights that during winter months, the combination of cold weather (which shrinks arteries) and thick blood leads to a spike in heart attacks specifically between 6:00 AM and 9:00 AM. This is a critical window of risk.
The “Natural Bypass” exists: You don’t always need surgery to improve blood flow. A therapy called EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) has been proven to increase Nitric Oxide and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), effectively creating new pathways for blood to flow around blockages. It also helps lower triglyceride levels by improving metabolism.
Women Are at Greater Risk: High triglycerides are often a stronger predictor of heart disease death in women than in men, especially for those over age 50 or those with diabetes.
Pancreatitis Link: While we focus on the heart, extremely high levels (over 500 mg/dL) can cause acute pancreatitis, a life-threatening inflammation of the pancreas, which further stresses the cardiovascular system.
To understand why High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack, we must first understand what they actually are. In the simplest terms, triglycerides are the energy reserve of your body.
Imagine your body is a car. It runs on fuel.
Glucose (Sugar): This is the fuel for “right now.” It gives you instant energy to walk, think, and work.
Triglycerides (Fat): This is the fuel for “later.” It is your body’s backup battery.
When you eat a meal, your body takes the calories it doesn’t need immediately and converts them into triglycerides. These are then stored in your fat cells (adipose tissue). Later, when you are sleeping or haven’t eaten for a few hours, hormones release these triglycerides back into your blood to give you energy.
This system works perfectly if you are active and burning off that energy. The problem arises when you keep filling the tank but never drive the car. If you eat more calories than you burn—especially from carbohydrates and sugars—your triglyceride levels shoot up. This is where the trouble begins, and where the risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack becomes real.
This is the most common confusion among patients. “My cholesterol is fine, so why am I at risk?” Both are lipids (fats) in your blood, but they have very different jobs.
Cholesterol: Think of this as a building block. Your body uses it to build cell walls, produce hormones (like testosterone and estrogen), and make Vitamin D. It is waxy and structural.
Triglycerides: Think of this as firewood. They are burned for energy.
The Dangerous Combination:
If you have high triglycerides (too much firewood) and high LDL cholesterol (too many building blocks) floating in your blood, they start to pile up. The triglycerides make the LDL particles smaller and denser. These tiny, dense particles act like shrapnel—they easily penetrate the walls of your arteries and get stuck there. This is a primary reason why High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
We have established that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack, but how does it happen? It is not just about fat blocking a pipe like a clogged drain. It is an active, biological process that damages your blood vessels from the inside out.
When triglyceride levels are high, they are carried through your blood inside transport vehicles called Lipoproteins (specifically VLDL – Very Low-Density Lipoprotein). These VLDL particles are rich in triglycerides.
As these particles travel through your bloodstream, they interact with the lining of your arteries (the endothelium). High levels of triglycerides trigger inflammation. Your body sees these fatty particles as intruders and sends white blood cells to attack them.
This battle between fat and immune cells creates a mess. It forms a sticky substance called plaque. Over time, calcium deposits into this plaque, making it hard and brittle. This process is called atherosclerosis. As the plaque grows, the artery narrows. This restricts the amount of oxygen-rich blood that can reach your heart muscle. This narrowing is the first step in the chain of events where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Not all plaque is the same. High triglycerides are often associated with the formation of “soft” plaque. Unlike hard, calcified plaque that is stable, soft plaque is like a pimple inside your artery. It has a thin covering and is filled with fat and inflammatory cells.
If your blood pressure spikes—perhaps during a cold winter morning or a moment of high stress—this soft plaque can rupture (burst).
This is the moment of crisis. When a plaque ruptures, your body tries to “heal” the injury by forming a blood clot.
The Triglyceride Effect: High triglycerides increase the viscosity (thickness) of your blood and increase the levels of clotting factors (like fibrinogen). This means your blood clots faster and harder than normal blood.
The Blockage: Because the blood is hyper-coagulable (prone to clotting), the clot grows rapidly. Within minutes, it can completely block the artery.
The Result: No blood can get to the heart muscle. The muscle begins to die. This is a Heart Attack. This illustrates precisely how High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Triglycerides and HDL (Good Cholesterol) act like a seesaw. When triglycerides go UP, HDL almost always goes DOWN.
HDL’s Job: HDL is like a garbage truck. It travels through your arteries, picks up excess cholesterol, and takes it back to the liver to be disposed of.
The Failure: When you have high triglycerides, you usually have low HDL. This means you have more plaque building up (because of the TGs) and fewer garbage trucks to clean it up (low HDL). This double mechanism significantly increases the risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Why do levels rise? While genetics play a role, lifestyle is the biggest driver. Understanding the causes is the first step to preventing the condition where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
This is the most critical point for diabetic patients. You might think eating fat raises triglycerides, but sugar and refined carbohydrates are often the bigger culprits.
The Physiology: When you eat sugar, white bread, pasta, potatoes, or white rice, your blood sugar spikes. Your pancreas releases insulin to manage it.
The Overflow: If you eat more carbs than you can burn for energy, your liver takes that excess sugar and turns it directly into triglycerides.
Fructose Warning: Fructose (found in added sugars, sodas, and fruit juices) is particularly dangerous because it bypasses the body’s normal fullness signals and goes straight to the liver to be turned into fat. This is a major driver of why High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack in modern diets.
If you carry excess weight around your stomach (a “spare tire”), you are at much higher risk. Abdominal fat is metabolically active—it churns out fatty acids that travel to the liver and increase triglyceride production. Obesity is strongly linked to the scenario where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
This is a cluster of conditions that occur together, increasing your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. High triglycerides are a defining feature of metabolic syndrome. If you have high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and excess body fat around the waist alongside high triglycerides, your risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack skyrockets.
Certain medicines you might be taking for other conditions can raise triglyceride levels as a side effect:
Steroids: Often used for inflammation.
Beta-blockers: Used for blood pressure (some older types).
Diuretics: Water pills.
Estrogen: Oral contraceptives or hormone therapy.
Retinoids: Used for skin conditions.
Immunosuppressants: Used after transplants.
An underactive thyroid slows down your body’s metabolism. This means your body breaks down fat more slowly, leading to higher levels of triglycerides and cholesterol circulating in the blood. Correcting thyroid levels is often necessary to reduce the risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Alcohol is extremely calorie-dense and high in sugar. For some people, even small amounts of alcohol can stimulate the liver to produce massive amounts of triglycerides. If you have high levels, alcohol can be a direct trigger for the event where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
To prevent the situation where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack, you must know your numbers. A simple blood test called a “Lipid Panel” will show you where you stand. You typically need to fast (no food) for 9-12 hours before this test for accurate results.
| Level Category | Range (mg/dL) | Range (mmol/L) | What This Means for You |
| Normal | Less than 150 | Less than 1.7 | Your risk is lower. Maintain your healthy lifestyle. |
| Borderline High | 150 – 199 | 1.8 – 2.2 | Warning Zone. You need to reduce sugar and carbs immediately. |
| High | 200 – 499 | 2.3 – 5.6 | Danger Zone. Your risk of heart disease is elevated. You need diet changes, exercise, and possibly supplements. |
| Very High | 500 or higher | 5.7 or higher | Critical Zone. High risk of Pancreatitis and immediate cardiovascular events. Urgent medical attention is required. |
The “Normal” range of 150 mg/dL applies to the general healthy population. If you already have heart disease, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome, your target should be lower. Ideally, you want your triglycerides to be below 100 mg/dL to truly minimize the residual risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Unlike high blood pressure, high triglycerides usually have no symptoms until the damage is done. This is why it is a “silent” killer. However, in cases of very high levels (genetic conditions), you might see:
Xanthomas: Small fatty deposits under the skin, often around the eyes or on elbows/knees.
Lipemia Retinalis: The blood vessels in the back of your eye may look white or creamy instead of red.
Recurrent Pancreatitis: Severe stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting.
We often think of heart attacks as random events, but biology has a rhythm. Research suggests that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack more frequently during specific times of the year and specific times of the day.
Statistics show a spike in heart attacks between 6:00 AM and 9:00 AM. Why?
Cortisol Surge: When you wake up, your body releases cortisol to help you get alert. Cortisol raises blood pressure and heart rate.
Platelet Stickiness: Your blood platelets are naturally “stickier” in the morning.
The Triglyceride Factor: If you have high triglycerides, your blood is already thicker (more viscous) than normal.
In winter, this risk multiplies. Cold weather causes vasoconstriction—your blood vessels narrow to preserve body heat.
The Physics: Imagine trying to pump thick oil (high triglyceride blood) through a narrow pipe (constricted artery). The pressure required is immense.
The Rupture: This increased pressure can cause the fragile plaque in your arteries to tear or rupture.
The Result: The clot forms, the artery blocks, and a heart attack occurs.
Patient Advice: If you have high triglycerides, be extremely careful on cold winter mornings. Do not jump out of bed and immediately go outside to shovel snow or exercise vigorously. Stay warm, hydrate with warm water to thin the blood, and allow your body to wake up slowly. This simple precaution can reduce the chance that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
When diet and lifestyle are not enough, or if levels are critically high, doctors prescribe medication. It is crucial to understand that while these drugs lower numbers, they also come with side effects.
Statins are the most common heart drug. They act by blocking an enzyme in the liver that produces cholesterol.
Impact on TGs: While mainly for LDL, potent statins can lower triglycerides by 20-40%.
Side Effects: Muscle pain, weakness, liver enzyme elevation, and a small increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Limitations: Statins lower the risk, but they do not eliminate the “residual risk” caused by triglycerides. Even on statins, High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack in many patients.
These are older drugs specifically designed to lower triglycerides.
Mechanism: They speed up the removal of triglycerides from the blood.
Impact: Can reduce levels by 30-50%.
Side Effects: They can cause stomach upset and gallstones. Importantly, taking Fibrates with Statins increases the risk of muscle damage significantly.19
Unlike store-bought fish oil, these are highly purified, prescription-strength forms of EPA (an omega-3 fatty acid).
Benefit: They lower triglycerides effectively without the muscle side effects of statins. Studies like REDUCE-IT have shown they reduce heart attacks in high-risk patients.
Research presented in late 2024 and 2025 points to new drugs like DR10624. This injectable medication targets multiple hormone receptors (FGF21, GLP-1) and has shown in trials to reduce triglycerides by over 70% in patients with severe levels. While promising, these are new and may be expensive.
For thousands of years, traditional medicine has managed blood lipids using nature. These remedies often work by improving liver function and reducing inflammation, targeting the root causes of why High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
Arjuna is perhaps the most celebrated herb in Ayurveda for the heart. It is the bark of the Arjuna tree.
Mechanism: It is a potent antioxidant and cardiac tonic. It strengthens the heart muscle, improving the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF).
Lipid Effect: Studies show it reduces total cholesterol and triglycerides while raising HDL. It helps reduce the oxidation of LDL, preventing plaque formation.3
How to use: Commonly available as a powder (Ksheerapak—boiled with milk) or capsules.
Garlic is not just a kitchen staple; it is powerful medicine.
The Active Agent: Allicin.
Mechanism: A 2024 meta-analysis confirmed that garlic supplementation significantly lowers triglyceride levels. It also acts as a natural blood thinner, preventing the platelets from clumping together to form the deadly clots that cause heart attacks.
Tip: To get the medicinal benefit, crush a clove of raw garlic and let it sit for 5 minutes before swallowing with water. Cooking destroys much of the Allicin.
Guggul is a resin (gum) from a tree, used traditionally for “Medoroga” (obesity and lipid disorders).
Mechanism: It contains guggulsterones, which increase the liver’s metabolism of LDL and triglycerides.
Caution: It stimulates the thyroid, which helps burn fat, but can interact with some heart medications. Always consult an Ayurvedic physician.
Homeopathy treats the patient’s constitution. Remedies like Cholesterinum (for liver congestion), Lycopodium (for digestive-linked lipid issues), and Crataegus (Hawthorn Berry – a heart tonic) are frequently used to support lipid management alongside lifestyle changes.
To help you decide the best path with your doctor, here is a comparison of the different ways to treat the risk where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
| Feature | Statins (Medical) | Fibrates (Medical) | Ayurveda (Natural) | EECP Therapy (Integrative) |
| Primary Target | LDL Cholesterol | Triglycerides | Metabolism & Doshas | Blood Flow & Vessel Health |
| TG Reduction | Moderate (20-40%) | High (30-50%) | Moderate (Slow & Steady) | Moderate + Improves HDL |
| Mechanism | Blocks liver enzyme | Increases fat breakdown | Antioxidant & Liver support | Shear Stress & Angiogenesis |
| Invasiveness | Oral Pill | Oral Pill | Oral Supplements | Non-Invasive (External) |
| Side Effects | Muscle pain, Liver stress | Gallstones, Stomach issues | Rare (if standardized) | None (Natural Action) |
| Best For | High LDL + TGs | Very High TGs (>500) | Prevention & Maintenance | Angina, Weak Heart, Diabetes |
For patients who want to treat the root cause of poor circulation without surgery, EECP (Enhanced External Counterpulsation) is a revolutionary option. While often used for chest pain (angina), its metabolic benefits directly combat the risk that High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack.
EECP is a non-invasive, outpatient therapy. You lie on a comfortable bed, and pneumatic cuffs (like large blood pressure cuffs) are wrapped around your calves, thighs, and buttocks. These cuffs inflate and deflate in precise synchronization with your heartbeat (using an ECG).
Diastole (Relaxation): When your heart relaxes, the cuffs inflate instantly from the bottom up. This squeezes oxygen-rich blood from your legs back up to your heart and vital organs.
Systole (Pumping): Just before your heart pumps, the cuffs deflate instantly. This creates a vacuum that makes it easier for your heart to pump blood out.
Increases Nitric Oxide: The rapid movement of blood creates “shear stress” or friction against the artery walls. This friction signals your arteries to release Nitric Oxide, a gas that dilates (widens) blood vessels and repairs the inner lining (endothelium). Healthy endothelium resists the sticking of triglycerides and plaque.
Angiogenesis (New Vessels): EECP stimulates the release of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor). This growth factor encourages the body to grow tiny new blood vessels (collaterals) around blocked arteries. It is literally a “natural bypass” created by your own body.
Metabolic Improvement: It acts like intensive exercise for your vascular system. It improves insulin sensitivity and helps mobilize triglycerides from fat stores to be burned for energy. Studies have shown improvements in lipid profiles (lower TGs, higher HDL) after a course of 35 sessions.
Anti-Inflammatory: Since High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack via inflammation, EECP’s proven ability to reduce inflammatory markers (like TNF-alpha) makes plaque more stable and less likely to rupture.
You cannot medicate your way out of a bad diet. To stop the cycle where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack, you must change the fuel you put in your body. The good news is that triglycerides respond very fast to diet changes—much faster than cholesterol.
Since your liver turns sugar into triglycerides, cutting carbohydrates is the most powerful tool you have.
Eliminate the “White Poisons”: Sugar, Maida (white flour), white rice, white bread, pasta, and potatoes.
The Fructose Danger: Avoid High Fructose Corn Syrup (found in sodas and processed snacks). Stop drinking fruit juice. Eat the whole fruit instead, but limit high-sugar fruits like mangoes, grapes, and bananas.
Switch to Complex Carbs: Eat Quinoa, Barley, Millets (Bajra, Jowar, Ragi), and Cauliflower “rice.” These release sugar slowly, preventing the insulin spike that triggers triglyceride production.
Fiber acts like a sponge in your intestines. It traps sugar and fat and slows their absorption.
Target: 25-30 grams per day.
Sources: Legumes (beans, lentils), Psyllium husk (Isabgol), Oats (steel-cut), and leafy green vegetables.
Don’t fear all fat, but fear the wrong fat.
Avoid Trans Fats: Found in bakery items (biscuits, cakes, puffs) and vanaspati/margarine. These are direct triggers for heart disease.
Embrace Omega-3s: Omega-3 fatty acids stop the liver from making triglycerides. Eat fatty fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines), Flaxseeds, Walnuts, and Chia seeds.
Cooking Oils: Use Mustard oil, Olive oil, or moderate amounts of Ghee. Avoid refined vegetable oils like sunflower or soybean oil which can be inflammatory in excess.
This is a powerful way to burn off the “firewood.” By restricting your eating window to 8-10 hours (e.g., eating only between 10 AM and 8 PM), you force your body to burn stored triglycerides for energy during the 14-16 hours of fasting.
The equation where High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack involves more than just food. Your lifestyle habits act as either accelerators or brakes on this process.
Triglycerides are energy. If you don’t use them, they store up.
Aerobic Exercise: Brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes a day burns triglycerides directly.
Resistance Training: Building muscle increases your metabolic rate, helping you burn fat even when you are sleeping.
Post-Meal Walk: A 10-minute walk immediately after meals helps shunt sugar into muscles instead of the liver, preventing triglyceride formation.
Stress is a chemical event. When you are stressed, your body releases Cortisol. Cortisol mobilizes sugar and fat into the bloodstream to provide energy for a “fight or flight” response. If you are stressed but sitting at a desk, that mobilized fat just circulates and clogs your arteries.
Solution: Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing are not luxuries; they are medical necessities. Studies presented in 2025 show that Yoga significantly reduces adverse cardiovascular events by lowering stress hormones.
Lack of sleep messes with your hunger hormones (Ghrelin and Leptin) and makes you crave sugar. It also keeps cortisol levels high. Getting 7-8 hours of quality sleep allows your body to regulate metabolism and clear out waste products from the brain and blood.
Que: Can High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack even if my cholesterol is normal?
Ans: Yes. This is known as “residual risk.” Even if your LDL (bad) cholesterol is low, high triglycerides can still cause inflammation in the arteries and make your blood thicker, leading to clots and heart attacks.
Que: What is the fastest way to lower triglycerides naturally?
Ans: The fastest method is to drastically cut down on sugars and refined carbohydrates (bread, rice, pasta, sweets) and eliminate alcohol. Combining this with 30-45 minutes of daily exercise can show significant reductions in just a few weeks.
Que: Is EECP therapy safe for someone with high triglycerides and diabetes?
Ans: Yes, EECP is FDA-approved and is particularly beneficial for diabetics. It improves insulin sensitivity and circulation, which helps the body process sugar and fats better, naturally lowering triglycerides over time.
Que: I have heard about “Morning Heart Attacks.” How do triglycerides affect this?
Ans: High triglycerides increase blood viscosity (thickness). In the early morning, especially in winter, your arteries naturally constrict (narrow). Pumping thick blood through narrow arteries puts immense strain on the heart, significantly increasing the risk of a heart attack between 6 AM and 9 AM.
Que: Can stress really raise my triglyceride levels?
Ans: Absolutely. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that tells your liver to release stored glucose and fat (triglycerides) into the bloodstream for energy. If this energy isn’t used physically, it remains in the blood, raising your levels.
Que: Are there any fruits I should avoid if I have high triglycerides?
Ans: Yes. You should limit high-sugar fruits like mangoes, grapes, bananas, and chikoo (sapodilla), as well as dried fruits. Strictly avoid fruit juices, as they are concentrated sugar. Stick to low-sugar fruits like berries, guava, and apples with skin.
Que: How does Garlic help with heart blockages and triglycerides?
Ans: Garlic contains a compound called Allicin. Research shows Allicin helps lower triglycerides, reduces LDL cholesterol, and importantly, prevents platelets from clumping together, which reduces the risk of blood clots forming over plaque.
Que: What is the difference between Angioplasty and EECP?
Ans: Angioplasty is an invasive procedure where a stent is placed inside an artery to prop it open mechanically. EECP is a non-invasive therapy that acts like a “natural bypass” by stimulating the body to grow new, natural blood vessels (collaterals) around blockages using increased blood flow and growth factors.
Que: Why are triglycerides dangerous for the pancreas?
Ans: When triglyceride levels are extremely high (usually over 500 mg/dL), the fat can clog the tiny capillaries in the pancreas. This causes toxic fatty acids to be released, damaging the pancreatic tissue and leading to Pancreatitis, a painful and potentially fatal inflammation.
Que: How often should I check my triglyceride levels if they are high?
Ans: If you are actively making lifestyle changes or taking medication, you should check your Lipid Profile every 3 to 6 months to monitor progress. Once your levels are stable and within the normal range, a yearly check-up is usually sufficient.
The question we started with was, “Can High Triglycerides Cause Heart Attack?” The evidence is undeniable. High triglycerides are not just a passive bystanders; they are active contributors to heart disease, driving inflammation, building plaque, and thickening the blood.
However, the power to change this trajectory is in your hands. Unlike some genetic conditions, high triglycerides are incredibly responsive to lifestyle changes. By reducing your sugar intake, moving your body, considering powerful natural allies like Arjuna and Garlic, and exploring non-invasive therapies like EECP, you can dramatically lower your risk.
Do not wait for a warning sign. The “silent” nature of triglycerides is what makes them dangerous. Check your numbers, consult your specialist, and start your journey toward a cleaner, healthier cardiovascular system today. Your heart is the engine of your life—keep the fuel clean.
NexIn Health is a pioneer in non-invasive cardiac and spine care, dedicated to helping patients reverse lifestyle diseases without surgery. With over 14 years of experience and having successfully consulted over 30,000 patients, we specialize in Integrated Heart Treatments. Our expert team utilizes FDA-approved EECP Therapy, advanced diagnostics, and holistic lifestyle management (Ayurveda & Nutrition) to treat the root causes of heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic disorders.
Take the first step towards a healthier heart today.
📞 Phone / WhatsApp: +91 9310145010
🌐 Website: www.nexinhealth.in
📧 Email: care@nxinhealth.in